On the outskirts of the Milky Approach, one of many rarest kinds of stars within the galaxy has simply turn out to be much more mysterious than it was earlier than.
Astronomers have used the Hubble and Gaia telescopes to review the environment of SGR 0501+4516, a sort of neutron star generally known as a magnetar. The investigation reveals that we nonetheless don’t have any clear concept of how magnetars type – the lead we thought we had on their delivery mechanism is totally unrelated to SGR 0501+4516.
Nonetheless, what the researchers did, or relatively, didn’t discover, means that we might have been improper about how we thought magnetars happened.
Neutron stars are among the many densest objects within the Universe, crushed out solely by black holes, and so they type in the same approach. When an enormous star runs out of gasoline to fuse in its core, its core can now not assist itself by the outward strain of fusion, and collapses below gravity in a violent occasion generally known as a core-collapse supernova.
A magnetar is just about the identical factor, with an added distinction: the magnetic area of a magnetar is probably the most highly effective recognized within the Universe, round a thousand times more powerful than a standard neutron star’s magnetic area, and a quadrillion times extra highly effective than Earth’s.
It isn’t clear how magnetars type, however, as a result of they’re a subspecies of neutron star, astronomers had thought that they need to type from core-collapse supernovae too. SGR 0501+4516 gave the impression to be proof of this.
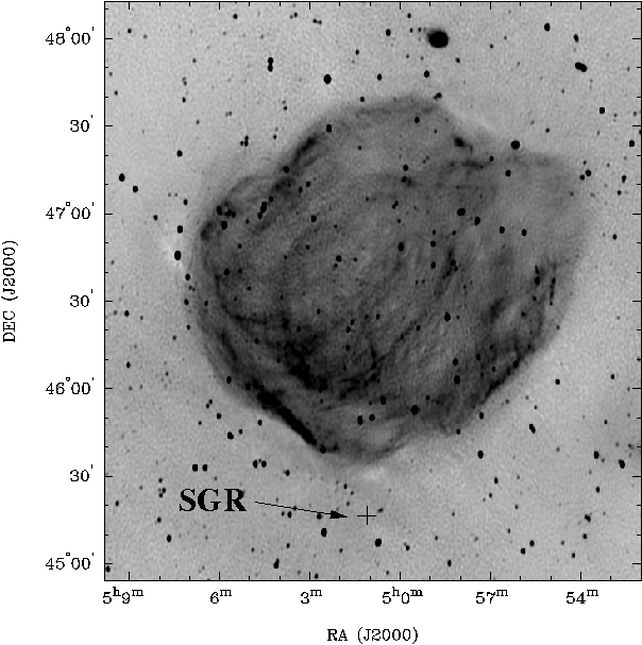
When huge stars go supernova, the proof hangs round for a while after within the type of a supernova remnant. SGR 0501+4516’s place could be very near a supernova remnant known as HB9. As well as, no different neutron stars have been detected in HB9’s neighborhood. So astronomers had thought that the two objects were related, which is actually a pretty fair assumption.
Now, the mixed observations of the Hubble Area Telescope and the recently retired Gaia mission have forged important doubt on this assumption.

Gaia was an area telescope whose mission was to exactly map the objects throughout the Milky Approach galaxy utilizing precision parallax measurements, together with positions in three dimensions and correct motions. Hubble pictures taken utilizing Gaia information as a reference body enabled a analysis staff led by astronomer Ashley Chrimes of the European Area Company to very finely map the motion of SGR 0501+4516 within the sky.
The speed and correct movement of the magnetar had been such that there isn’t any approach it may very well be related to HB9. As well as, there are not any different supernova remnants close by that may very well be associated to SGR 0501+4516.
This might imply one in every of a number of issues.
The primary is that the magnetar, considered round 20,000 years previous, is definitely far older – sufficiently old for its related supernova remnant to have dissipated. The issue with that is that magnetars are considered a brief part within the lifetime of a neutron star, lasting a few tens of thousands of years earlier than settling down right into a extra staid existence.
The opposite possibility is that SGR 0501+4516 didn’t type through core-collapse supernova, however a merger of some variety. This might contain two low-mass neutron stars colliding; or it may very well be one thing else, a white dwarf. That is a step down from neutron stars on the density scale, an object that kinds from the collapsed core of a low-mass star, relatively than an enormous one.
White dwarfs generally have binary companions from which they slurp mass. If a white dwarf slurps up an excessive amount of mass, it turns into unstable.
“Usually, this state of affairs results in the ignition of nuclear reactions, and the white dwarf exploding, leaving nothing behind,” explains astronomer Andrew Levan of Radboud College within the Netherlands and the College of Warwick within the UK.
“Nevertheless it has been theorised that below sure circumstances, the white dwarf can as an alternative collapse right into a neutron star. We predict this is perhaps how SGR 0501 was born.”
It is troublesome to gauge, actually. What does appear clear, nevertheless, is {that a} core-collapse supernova is now the least possible rationalization for the magnetar’s formation, making SGR 0501+4516 the very best candidate out of the fewer-than-30 magnetars within the Milky Approach for a non core-collapse formation pathway.
And that’s extremely cool.
“Magnetar delivery charges and formation situations are among the many most urgent questions in high-energy astrophysics,” says astronomer Nanda Rea of the Institute of Area Sciences in Spain, “with implications for lots of the Universe’s strongest transient occasions, reminiscent of gamma-ray bursts, superluminous supernovae, and fast radio bursts.”
The findings have been revealed in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Associated Information
Source link