Whereas america and a lot of the European Union have shrugged off the pandemic recession and restarted their financial engines, Germany stays idled.
Its economic system shrank slightly in 2024, after adjusting for rising costs. Forecasts for this 12 months don’t look a lot better.
And different measures look even worse. They present an economic system quickly sliding backward, stunning declines which have emerged as one of many largest points within the parliamentary election set for Sunday.
Supply: Eurostat
Be aware: The horizontal axis exhibits the proportion distinction between Germany and the full for the 27 nations within the European Union in the latest information. The vertical axis exhibits how that metric has modified in Germany over the latest 12 months of information. Each axes are plotted on a logarithmic scale.
The scenario is nothing wanting a nationwide disaster. A rustic that has lengthy prided itself on its work ethic and its manufacturing would possibly is now watching world rivals race previous it.
“Financial coverage in Germany is in tatters,” Stefan Pallesch, a kitchen provide retailer proprietor from the nation’s wine area mentioned this month on the sidelines of a political rally within the city of Stromberg. He went on to record a number of industries in disaster, together with building, conventional automaking, and electrical autos.
Enterprise leaders and lots of nervous voters use the identical phrase when describing what’s gone fallacious: competitiveness. They really feel as if they’re a soccer star who all of a sudden can’t discover the online, or a marathoner who can’t sustain with the lead group. They usually really feel prefer it’s occurred nearly in a single day.
“I positively imagine that we will compete,” mentioned Christian Klein, the C.E.O. of German-based software program big SAP, “however some fundamentals have to vary.”
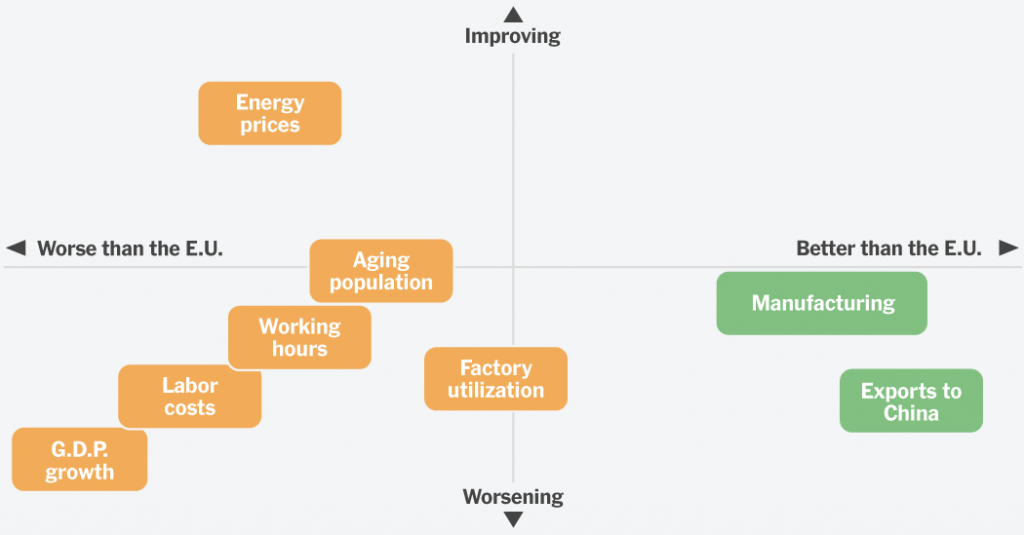
The charts under present simply what it seems like when an economic system quickly loses its edge. They inform a stark story of business woe and workforce challenges, with few alternatives for a near-term turnaround of the type German politicians are promising as they vie for the chancellorship.
‘Caught in stagnation’
Within the large image, it’s unattainable to overlook Germany’s struggles. Begin with progress, which helped make Germany the world’s third-largest economic system however has solely cracked 2 % per 12 months as soon as since 2017. After adjusting for rising costs, the German economic system is not any bigger immediately than it was 5 years in the past. Authorities forecasters predict an anemic 0.3 % progress fee this year.
Germany’s financial progress has stagnated.
Greater than the E.U. Decrease than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits year-on-year financial progress, adjusted for inflation.
“Germany is caught in stagnation,” the financial minister, Robert Habeck, mentioned late final month.
That’s partly as a result of German leaders made an enormous wager on globalization that has not but paid off. Even with a big client base at house, German firms depend on international markets for gross sales progress. Greater than four-fifths of the German economic system depends upon trade, in comparison with a few quarter of the American economic system. The specter of a world commerce struggle, spurred by tariffs from the Trump administration, looms over every part.
The market that when regarded most promising, China, more and more seems fraught. German exports to China peaked in 2022 and have been declining, although China is rising. That has drained gas for progress. German firms haven’t but discovered different markets to exchange their slowing Chinese language gross sales.
Germany exports extra to China in comparison with different E.U. economies, however exports are declining.
Greater share of G.D.P. from exports to China
Be aware: Exhibits exports to China as a share of G.D.P.
Excessive prices, low demand
A lot of Germany’s financial id is wrapped up in its factories: automobiles, chemical substances, prescription drugs, even espresso makers. That makes the sector’s struggles all of the extra painful.
Manufacturing continues to be the spine of the economic system, however it’s declining.
Greater share of G.D.P. from manufacturing than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits the share of G.D.P. contributed by the manufacturing sector.
Manufacturing is falling as a driver of Germany’s economic system. Whereas German factories was once the envy of Europe, they aren’t anymore. They’re not even above-average, by way of output.
After many years of German manufacturing buzzing at a lot larger charges than its European counterparts, Germany idled extra of its manufacturing traces final 12 months than the European Union as a complete.
Germany’s factories have extra idle capability, and are actually falling behind Europe’s.
Much less idle capability than the E.U. Extra idle capability than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits industrial capability utilization.
Manufacturing facility homeowners, executives and employees all identify the identical perpetrator for that slide: hovering vitality prices. It takes lots of energy to run a manufacturing facility, and Germans pay extra for it than their neighbors do. German politicians pushed the country earlier than the pandemic to shutter its nuclear energy vegetation and ramp up imports of pure fuel from Russia. When Russia invaded Ukraine, the circulate of fuel stopped and vitality prices soared.
Germany’s vitality prices stay excessive, although are easing.
Cheaper than the E.U. Costlier than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits the worth per kilowatt-hour for customers utilizing between 70,000 MWh and 149,999 MWh, excluding taxes and levies.
The nation has quickly invested in renewable sources like wind and photo voltaic, however the nation’s excessive vitality prices stay an enormous burden on firms attempting to compete with rivals in Europe, Asia and America, the place electrical energy prices much less.
A much less aggressive workforce
Together with excessive vitality prices, economists and enterprise leaders complain that traits of Germany’s labor pool put it at an obstacle. German employees are costlier than their counterparts throughout Europe, largely as a result of hourly wages are significantly higher than in peer nations.
Germany’s labor prices are excessive, and nonetheless rising.
Greater than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits the price of using a employee, together with compensation of staff, taxes, and subsidies.
And as a complete, its inhabitants works much less.
Germans work much less per week than these within the E.U., and their hours are nonetheless falling.
Decrease working hours than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits the typical variety of hours labored per week by full-time staff.
The nation has additionally skilled shifts in employee preferences, usually influenced by authorities insurance policies.
In 1991, shortly after the autumn of the Berlin Wall, about 14 % of Germans labored part-time. That quantity has greater than doubled, to 30 percent.
Even full-time employees are logging fewer hours. And Germany has seen a surge within the variety of days that employees name out sick, with a median of twenty-two recorded in 2023, based on the German Financial Institute.
Politicians throughout the political spectrum agree the nation wants extra employees, and can for many years to come back. Germany’s post-war child growth got here later than America’s, and it is just starting to see the wave of employee retirements from that technology.
Germany has extra retirees per employee than the E.U.
Older than the E.U.
Be aware: Exhibits the variety of folks aged 65 or over as a proportion of the inhabitants aged 15 to 64.
Conservative politicians within the chancellor race have promised to curb authorities welfare funds to individuals who can work, however select to not. Economists say the nation’s insurance policies, and its social norms, discourage women in particular from working extra.
The workforce disaster would look even worse if not for the thousands and thousands of refugees and different migrants Germany has taken in from nations like Syria, Afghanistan and Ukraine over the previous decade. Economists say they’ve helped fill within the holes left by retirements and the shift to part-time work.
Final 12 months, researchers on the Group for Financial Cooperation and Growth in Paris reported that Germany had a 70 % employment fee for immigrants in 2022. That was considerably larger than most different European Union nations.
The migration surge, although, has additionally strained German society and emerged as a high voting problem. Significantly in elements of the nation the place manufacturing facility manufacturing has fallen, voters have embraced politicians who promise to dam new refugees and deport these already there.
For some voters, it’s a grievance certain tightly to their expertise of financial decline: the nation, they are saying, now not seems just like the Germany they grew up in, and so they need the previous one again.
Source link